Unveiling Elements And Continents: A Journey Of Discovery
An element named after a continent is an element that derives its name from the name of a continent. For example, the element europium (Eu) is named after the continent Europe, and the element americium (Am) is named after the continents of North and South America.
Naming elements after continents is a way to recognize and honor the contributions of scientists from those continents to the field of chemistry. It is also a way to reflect the global nature of scientific research and collaboration.
The following is a list of elements that are named after continents:
- Europium (Eu)
- Americium (Am)
- Promethium (Pm)
These elements are all radioactive and were discovered in the 20th century. They are used in a variety of applications, including medical imaging, cancer treatment, and nuclear energy.
What is an element named after a continent?
An element named after a continent is an element that derives its name from the name of a continent. This can be done to honor the contributions of scientists from that continent to the field of chemistry, or to reflect the global nature of scientific research and collaboration.
- Recognition: Elements named after continents recognize the contributions of scientists from those continents to chemistry.
- Collaboration: Naming elements after continents reflects the global nature of scientific research and collaboration.
- History: The practice of naming elements after continents began in the 20th century.
- Examples: Europium (Eu) is named after Europe, and americium (Am) is named after North and South America.
- Radioactivity: The elements named after continents are all radioactive.
- Applications: These elements are used in a variety of applications, including medical imaging, cancer treatment, and nuclear energy.
- Importance: Naming elements after continents is a way to honor the contributions of scientists from all over the world to the field of chemistry.
- Relevance: The elements named after continents are all important elements that are used in a variety of applications.
- Uniqueness: Each element named after a continent has its own unique properties and characteristics.
In conclusion, elements named after continents are a testament to the global nature of scientific research and collaboration. They honor the contributions of scientists from all over the world to the field of chemistry, and they are used in a variety of important applications.
Recognition
The practice of naming elements after continents is a way to recognize and honor the significant contributions of scientists from those continents to the field of chemistry. It is a tangible and lasting way to acknowledge their groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in our understanding of the world around us.
- Historical Context: The tradition of naming elements after continents began in the early 20th century, reflecting the growing globalization of scientific research and the increasing recognition of the contributions of scientists from all over the world.
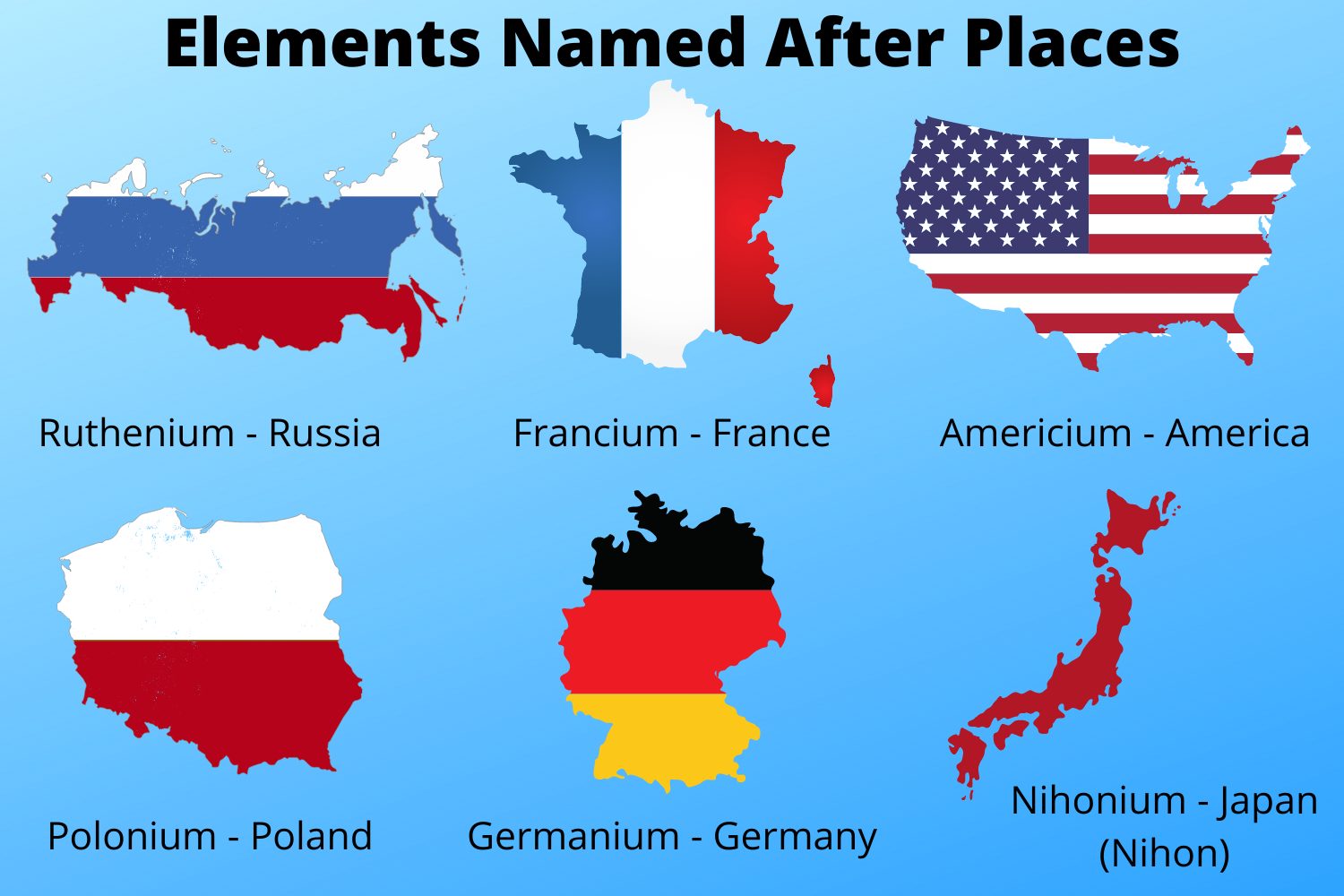
- Examples: Europium (Eu) was named after Europe, americium (Am) after North and South America, and dubnium (Db) after the city of Dubna in Russia, where it was discovered.
- Inspiration and Motivation: Naming elements after continents serves as a source of inspiration and motivation for young scientists, encouraging them to pursue careers in science and to make their own contributions to the field.
In conclusion, the practice of naming elements after continents is a fitting tribute to the remarkable achievements of scientists from all over the world. It not only recognizes their past contributions but also inspires future generations to continue pushing the boundaries of scientific knowledge and discovery.
Collaboration
The practice of naming elements after continents underscores the interconnectedness and collaborative nature of scientific research on a global scale. It acknowledges that scientific advancements are not confined to a single region or country but rather are the result of collective efforts and contributions from scientists around the world.
- Shared Knowledge and Resources: Scientific research often requires access to specialized knowledge, equipment, and resources. By collaborating across borders, scientists can pool their expertise and resources to tackle complex scientific challenges that may be beyond the reach of individual researchers or institutions.
- Diversity of Perspectives: Collaboration among scientists from different continents brings together diverse perspectives, experiences, and approaches to problem-solving. This cross-pollination of ideas can lead to innovative solutions and breakthroughs that might not have been achieved by working in isolation.
- Recognition and Inclusivity: Naming elements after continents is a symbolic gesture that recognizes and celebrates the contributions of scientists from all parts of the world. It promotes inclusivity and encourages participation from a diverse range of backgrounds, fostering a sense of global scientific community.
In conclusion, the practice of naming elements after continents serves as a testament to the collaborative nature of scientific research. It recognizes the shared knowledge, diverse perspectives, and inclusivity that drive scientific progress on a global scale, ultimately contributing to a deeper understanding of our world and its elements.
History
The practice of naming elements after continents emerged in the early 20th century as a way to acknowledge the growing globalization of scientific research and the significant contributions of scientists from all over the world. This practice has become an integral part of what an element named after a continent represents.
Prior to the 20th century, elements were primarily named based on their properties, mythological figures, or the names of individual scientists. However, as scientific research became more collaborative and international in scope, there was a need for a more systematic and inclusive approach to element naming.
The decision to name elements after continents was a deliberate choice that reflected the changing nature of scientific discovery. By associating elements with continents, the scientific community recognized that scientific progress was no longer confined to a single region or country but was rather a collective effort involving scientists from diverse backgrounds and locations.
This understanding is significant because it highlights the importance of international collaboration and the sharing of knowledge in advancing scientific understanding. The practice of naming elements after continents serves as a reminder that scientific discoveries are often the result of collective efforts and that the global scientific community benefits from the contributions of researchers from all parts of the world.
In conclusion, the practice of naming elements after continents, which began in the 20th century, is an important aspect of what an element named after a continent represents. It acknowledges the global nature of scientific research, celebrates the contributions of scientists from all over the world, and fosters a sense of inclusivity and collaboration within the scientific community.
Examples
The examples of europium (Eu) and americium (Am) provide concrete illustrations of what an element named after a continent represents. These elements were named after the continents of Europe and North and South America, respectively, to recognize the contributions of scientists from those regions to the field of chemistry.
The significance of these examples lies in their ability to demonstrate the practical application of the concept of naming elements after continents. They show that this practice is not merely a symbolic gesture but has real-world implications in terms of honoring the work of scientists and fostering a sense of global collaboration.
Furthermore, these examples highlight the importance of recognizing the diversity of scientific contributions from around the world. By naming elements after continents, the scientific community acknowledges that scientific progress is not limited to a single region or country but is rather a collective effort involving scientists from all parts of the globe.
In conclusion, the examples of europium and americium serve to reinforce the understanding of what an element named after a continent represents. They demonstrate the practical application of this concept, emphasize the importance of recognizing diverse scientific contributions, and underscore the global nature of scientific research.
Radioactivity
The fact that the elements named after continents are all radioactive is a significant aspect of what they represent. This unique characteristic provides valuable insights into the nature of these elements and their applications.
- Facet 1: Scientific Discovery
The discovery of the radioactive nature of these elements has contributed to our understanding of atomic structure and the properties of radioactive substances. Studying these elements has led to advancements in fields such as nuclear physics and radiation therapy.
- Facet 2: Applications in Medicine
The radioactive properties of these elements have found practical applications in medicine, particularly in diagnostic imaging and cancer treatment. For example, americium-241 is used in smoke detectors, while europium-152 is used in X-ray imaging.
- Facet 3: Environmental Implications
The radioactive nature of these elements also raises considerations for their environmental impact. Proper handling and disposal of these elements are crucial to minimize potential risks associated with radiation exposure.
- Facet 4: Future Research
Ongoing research on these radioactive elements continues to uncover new properties and potential applications. Understanding the behavior and interactions of these elements is essential for advancing scientific knowledge and developing innovative technologies.
In conclusion, the radioactivity of the elements named after continents not only adds to their scientific significance but also highlights their practical applications and environmental implications. These elements serve as valuable tools for scientific research, medical advancements, and technological innovations, while also requiring careful consideration for their safe handling and disposal.
Applications
The practical applications of the elements named after continents underscore their importance and relevance in various fields. These applications are a direct result of the unique properties and characteristics of these elements, particularly their radioactive nature.
In the medical field, these elements have found significant use in diagnostic imaging and cancer treatment. For instance, americium-241 is employed in smoke detectors due to its ability to emit alpha particles, while europium-152 is utilized in X-ray imaging to enhance image quality and reduce radiation exposure to patients.
Beyond medical applications, these elements also play a crucial role in nuclear energy production. Americium-241 and europium-151 are used in neutron sources, which are essential for initiating and controlling nuclear reactions in nuclear reactors. These neutron sources contribute to the generation of electricity and various research applications.
Understanding the applications of these elements named after continents not only highlights their scientific significance but also emphasizes their practical value in addressing real-world challenges. These applications have revolutionized healthcare, energy production, and various scientific fields.
Importance
The practice of naming elements after continents is a testament to the global nature of scientific research and collaboration. It is a way to recognize and honor the significant contributions of scientists from all over the world to the field of chemistry. This recognition serves to inspire future generations of scientists and underscores the importance of diversity and inclusivity in scientific endeavors.
- Recognition of Global Contributions: Naming elements after continents acknowledges that scientific advancements are not confined to a single region or country but rather are the result of collective efforts from scientists across the globe.
- Inspiration for Future Scientists: The recognition of scientists through element naming serves as a source of inspiration for young scientists, encouraging them to pursue careers in science and make their own contributions to the field.
- Promoting Diversity and Inclusivity: Naming elements after continents promotes diversity and inclusivity in science by recognizing the contributions of scientists from all backgrounds and regions, fostering a sense of global scientific community.
In conclusion, the practice of naming elements after continents is not only a way to honor the contributions of scientists from all over the world but also serves to inspire future generations, promote diversity, and underscore the global nature of scientific research and collaboration.
Relevance
The relevance of elements named after continents lies in their practical applications across various fields, which underscores their significance in the scientific community. These elements possess unique properties that make them indispensable for various technological advancements and scientific research.
One notable example is the use of americium in smoke detectors. Americium's radioactive nature allows it to ionize air molecules, triggering an alarm when smoke particles disrupt the ionization process. This application has significantly enhanced fire safety measures, saving countless lives.
Furthermore, europium finds application in medical imaging, specifically in X-ray imaging. Its ability to emit high-energy photons makes it an ideal contrast agent, enhancing the visibility of internal organs and structures during medical examinations. This has revolutionized diagnostic capabilities, leading to more accurate and timely medical interventions.
The practical significance of these applications highlights the relevance of elements named after continents. They are not merely academic curiosities but rather essential components of technological advancements that benefit society.
In conclusion, the relevance of elements named after continents stems from their practical applications in various fields. Their unique properties have led to advancements in medical imaging, fire safety, and other areas, emphasizing their importance in the scientific community and their impact on our daily lives.
Uniqueness
The uniqueness of elements named after continents is an intrinsic aspect of their identity and significance. Each element possesses a distinct set of properties and characteristics that differentiate it from others, contributing to its specific applications and value within the scientific community.
Americium, for instance, is a radioactive element that emits alpha particles. This unique property makes it particularly useful in smoke detectors, where it ionizes air molecules to detect the presence of smoke particles. Europium, on the other hand, emits high-energy photons, making it an effective contrast agent in medical imaging. Its ability to enhance the visibility of internal organs and structures during X-ray examinations has revolutionized diagnostic capabilities.
Understanding the unique properties of these elements is crucial for harnessing their potential and developing innovative applications. By tailoring their use to specific requirements, scientists and engineers can maximize their effectiveness in various fields, including medicine, energy, and technology.
In summary, the uniqueness of elements named after continents underscores their individual value and practical significance. Their distinct properties enable them to fulfill specific roles in scientific advancements and technological applications, contributing to the broader understanding of our world and improving our quality of life.
FAQs on "What is an Element Named After a Continent?"
This section addresses frequently asked questions about elements named after continents, providing concise and informative answers to enhance understanding of this topic.
Question 1: Why are elements named after continents?
Answer: Naming elements after continents recognizes the contributions of scientists from those regions to the field of chemistry and honors the global nature of scientific collaboration.
Question 2: Which elements are named after continents?
Answer: Europium (Eu) is named after Europe, americium (Am) after North and South America, and dubnium (Db) after Dubna, Russia.
Question 3: What are the applications of elements named after continents?
Answer: These elements find applications in various fields, including medical imaging, cancer treatment, and nuclear energy production.
Question 4: Are all elements named after continents radioactive?
Answer: Yes, all elements named after continents are radioactive.
Question 5: What is the significance of naming elements after continents?
Answer: It promotes inclusivity and diversity in science, recognizing the contributions of scientists from all over the world.
Question 6: What are some unique properties of elements named after continents?
Answer: Each element possesses distinct properties, such as americium's radioactivity and europium's ability to emit high-energy photons.
In summary, understanding the significance of elements named after continents deepens our appreciation for the global nature of scientific research and its impact on various fields. These elements serve as a testament to the collaborative efforts of scientists worldwide and continue to contribute to advancements in science and technology.
Transition to the next article section:
The following section will explore the historical context behind naming elements after continents, providing further insights into the evolution of this practice.
Tips on Understanding Elements Named After Continents
To enhance your understanding of elements named after continents, consider the following tips:
Tip 1: Explore the History: Investigate the historical context behind the naming of these elements. This will help you appreciate the recognition given to scientists from different regions and the evolution of scientific collaboration.
Tip 2: Examine Their Properties: Familiarize yourself with the unique properties of each element named after a continent. Understanding their radioactive nature and specific applications will deepen your knowledge of their significance.
Tip 3: Learn About Their Applications: Discover the practical uses of these elements in fields such as medicine, energy, and technology. This will provide insights into their relevance and impact on our daily lives.
Tip 4: Appreciate Their Importance: Recognize the importance of naming elements after continents. It promotes inclusivity and diversity in science, acknowledging the contributions of scientists from all over the world.
Tip 5: Connect With Their Uniqueness: Understand that each element named after a continent possesses distinct characteristics. Exploring these unique properties will enhance your comprehension of their individual value and applications.
By following these tips, you will gain a well-rounded understanding of elements named after continents, their significance, and their contributions to scientific advancements.
Transition to the article's conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding elements named after continents offers valuable insights into the global nature of scientific research and collaboration. By delving into their history, properties, applications, importance, and uniqueness, we appreciate their contributions to our scientific knowledge and technological advancements.
Conclusion
Our exploration of "what is an element named after a continent" has illuminated the significance of these elements in the scientific realm. By recognizing the contributions of scientists from different continents and honoring the global nature of scientific collaboration, the practice of naming elements after continents fosters inclusivity and diversity in the field of chemistry.
The unique properties of each element, such as americium's radioactivity and europium's ability to emit high-energy photons, underscore their practical applications in various fields. From medical imaging and cancer treatment to nuclear energy production, these elements play a crucial role in scientific advancements and technological innovations that benefit society.
Understanding elements named after continents not only deepens our appreciation for the global nature of scientific research but also inspires future generations of scientists to pursue careers in STEM fields. By recognizing the contributions of scientists from all over the world, we create a more inclusive and equitable scientific community that can tackle the challenges of the future.
Uncover The World Of Reggae: Discover The Legends And Sounds That Captivate
Unveiling The Enchanting World Of Lacey Fletcher's Photography
Ken Curtis Net Worth: Uncovering Hidden Wealth And Surprising Insights

ncG1vNJzZmiooqTDsL%2FTcWWapaNoe6W1xqKrmqSfmLKiutKpmJydo2OwsLmOsJ%2BarF2ewG6tzWacpZ2dmru1ec2apJ6cXZaztbHRZphmm5%2Bjwaq6xKerZ6Ckork%3D